Blog Details

In the field of international logistics, the size and capacity of containers are crucial factors in planning and executing the transportation of goods. Understanding these dimensions is not only vital for ensuring the safe transit of cargo but also helps in optimizing transportation costs and efficiency. In this blog post, we will delve into the various sizes and capacities of containers and how they impact international logistics and cargo transportation.
Standardization of Container Sizes
The standardization of container sizes has made global trade more efficient. The most common sizes are the 20-foot and 40-foot-long containers, but there are other sizes and types for specific needs.
Standard Dry Containers
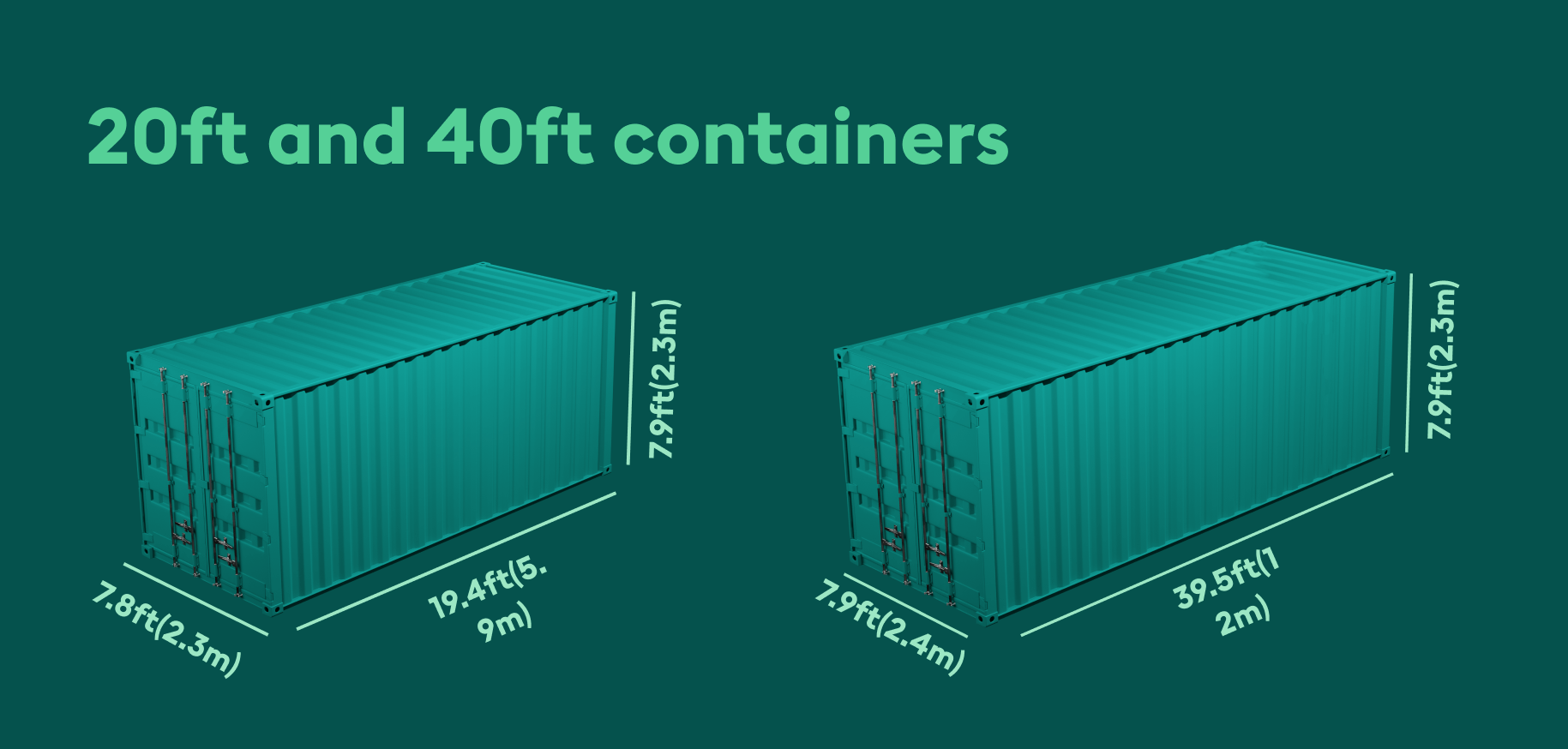
20-foot Containers: Standard length of 19.5 feet (about 5.9 meters), width of 7.8 feet (2.3 meters), and typical height of 7.9 feet (2.4 meters).
40-foot Containers: These containers are double the length of the 20-foot containers, with the same width and height.
High Cube Containers
40-foot High Cube Containers: Same length as standard 40-foot containers but with an increased height of 9.5 feet (2.9 meters), designed to accommodate larger volume cargo.
Specialized Containers
Including open-top, flat rack, and refrigerated containers, used for transporting special types of cargo such as over-height, over-width, or temperature-controlled goods.
?
?
Capacities of Containers
The capacity of a container directly affects its loading capability. For example:
20-foot Containers: Have a capacity of about 33 cubic meters (approximately 1,172 cubic feet).
40-foot Containers: Have a capacity of about 67 cubic meters (approximately 2,390 cubic feet).
40-foot High Cube Containers: Offer larger capacity, around 76 cubic meters (approximately 2,700 cubic feet).
Importance of Container Sizes and Capacities
Choosing the right container size and type is crucial for ensuring efficient and cost-effective transportation of goods. For instance, for large-volume but lightweight cargo, opting for high-cube containers might be more economical. For heavy cargo, it's important to ensure the container's weight capacity meets the requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the sizes and capacities of containers is fundamental for any company involved in international trade and logistics. Choosing the right container can maximize transportation efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure the safety of goods during global transit. As international trade continues to evolve, the demand and innovation in containers are also growing, which will further influence future trends in the logistics industry.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details
In the realm of international maritime shipping, the Bill of Lading (BOL) is an essential legal document. It serves not only as a receipt for the shipment of goods but also as a proof of ownership, in addition to being a key component of the contract of carriage between the shipper and carrier. Understanding the details within a BOL is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of international trade. In this blog post, we will delve into the important elements of the Bill of Lading and its role in maritime shipping.
Basic Functions of the Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading has three primary functions: it acts as a receipt for the shipment of goods, evidencing that the cargo has been loaded on board as per agreed terms; it serves as evidence of the contract of carriage, detailing the terms and conditions under which the goods are transported; and it is a document of title for the goods, which can be transferable.

?
Key Elements of the Bill of Lading
Shipper and Consignee Information
The BOL lists the details of the shipper (sender) and consignee (receiver). This information is crucial for customs clearance and delivery of goods.
Description of Goods
This includes the type, quantity, weight, and volume of the goods. Accurate descriptions are vital for customs declarations, insurance, and handling of the cargo.
Loading and Discharge Ports
The Bill of Lading specifies the ports of loading and discharge, essential for planning the transportation route.
Terms of Carriage and Charges
The BOL details the terms of carriage, including freight charges, surcharges, and payment conditions.
Bill of Lading Number
Each BOL has a unique number used for tracking and managing the cargo.
Types of Bills of Lading
Straight Bill of Lading
A straight BOL is used when the goods are to be delivered directly to the specified consignee without a change of ownership.
Transshipment Bill of Lading
This type is used when goods need to be transferred to another vessel during the journey.
Order Bill of Lading
An order BOL is a transferable document and can be endorsed to another party.
Legal Significance of the Bill of Lading
The Bill of Lading is a legally binding document, critical in resolving issues such as loss, damage to the cargo, or disputes in transportation.
Conclusion
The Bill of Lading plays an extremely important role in international maritime shipping. For businesses or individuals engaged in international trade, understanding every detail of the BOL is vital to ensure that your goods are transported safely, punctually, and in compliance with regulations. Proper handling of the Bill of Lading not only helps in avoiding potential legal risks but also ensures the smooth and efficient progress of the entire transportation process.
?

About Company
Wing Shipping offers various logisticssolutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea, and rail freight. We promote tradebetween China and the world, contributingto the development of your business.
Blog Details

In international trade, the Certificate of Origin (CO) is a crucial document vital for the smooth execution of cross-border transactions. It serves not only as an essential proof of trade but also, in many cases, as a requisite for customs clearance and the implementation of trade agreements. In this blog, we will delve into the definition of CO, its importance, and how to properly handle this key document.
What is a Certificate of Origin (CO)?
A Certificate of Origin is a formal document issued by an authorized institution or organization in the exporting country, certifying the origin of the goods. It indicates the country where the goods were manufactured, produced, or processed and is an indispensable part of international trade.

?
Why is CO so Important?
Customs Requirement: Many countries' customs authorities require a CO for imported goods to determine compliance with import regulations and to calculate import duties and tariffs.
Trade Agreements: CO is used to ascertain whether goods qualify under specific trade agreements or Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), allowing for tariff concessions.
Market Access: Some countries have restrictions or bans on goods from certain nations, making CO a crucial proof of legality.
Commercial Trust: CO provides transparency about the origin of goods to buyers, enhancing trust between international trading parties.
How to Obtain a CO?
Determine the Requirement: First, ascertain whether the destination country requires a CO and if there are specific formats or stipulations.
Submit Documentation: Submit the required documents, such as commercial invoices and packing lists, to the issuing authority in the exporting country.
Official Approval: The issuing authority will review the submitted documents and issue the CO after confirming their accuracy.
Be Mindful of Timeliness: Ensure the CO is current as some countries have strict validity requirements for COs.
Points to Note
Accuracy: Ensure all information is accurate and error-free, as mistakes can lead to customs clearance denials.
Compliance: Adhere to the legal regulations of the destination country and international trade agreements.
Stay Updated: Keep abreast of changes in trade policies and agreements to update your knowledge and practices related to CO.
Conclusion
In international trade, a Certificate of Origin is more than just a simple document; it involves the legality of goods, tariff benefits, and market access. For exporters, understanding and correctly handling CO is key to ensuring smooth transactions. By diligently managing each CO, businesses can better protect their interests in the complex international marketplace and establish more robust commercial relationships.
?

About Company
Wing Shipping offers various logisticssolutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea, and rail freight. We promote tradebetween China and the world, contributingto the development of your business.
Blog Details

In the complex world of international shipping, navigating the customs clearance process is a crucial step that can significantly impact the efficiency and success of global trade operations. Customs clearance involves the preparation and submission of documentation required to facilitate the export or import of goods, followed by the approval of these goods by the local customs authority. This blog aims to demystify the customs clearance process in international shipping, providing insights into how it works and tips for smooth clearance.
Understanding the Customs Clearance Process
Customs clearance is a mandatory process for all goods entering or leaving a country. It involves the assessment and evaluation of the goods to ensure they comply with the local laws and regulations, including the payment of relevant tariffs and taxes.
?

?
Key Steps in the Customs Clearance Process
Documentation Preparation
The first step involves preparing and submitting all necessary documents, which typically include the Bill of Lading, Commercial Invoice, Packing List, and, in some cases, specific permits or certificates.
Duty Assessment
Customs authorities assess the duties and taxes applicable based on the value, classification, and origin of the goods. This assessment is crucial in determining the cost of importing goods.
Goods Inspection
Some shipments may be subjected to physical inspection to verify the contents align with the documentation. Inspections can be random or triggered by specific concerns.
Duty Payment
Once the duties and taxes are assessed, payment must be made to the customs authorities. This step is essential for the release of the goods.
Release of Goods
After all duties are paid and compliance with customs regulations is confirmed, goods are released for delivery to the final destination.
Best Practices for Smooth Customs Clearance
Accurate Documentation
Ensure all documents are accurate, complete, and submitted promptly. Discrepancies can lead to delays and additional charges.
Understand Tariff Codes
Proper classification of goods using the correct Harmonized System (HS) codes helps in accurate duty assessment.
Stay Informed of Regulations
Keeping up-to-date with changes in customs regulations and trade agreements is vital to avoid non-compliance.
Work with Experienced Professionals
Partnering with experienced customs brokers or freight forwarders can streamline the process, especially for complex shipments.
Plan for Delays
Always account for potential delays in customs clearance when planning logistics to avoid disruptions in the supply chain.
Conclusion
Customs clearance is an integral part of international shipping that requires careful attention to detail and compliance with regulations. By understanding the customs clearance process and employing best practices, businesses can ensure a more seamless and efficient movement of goods across borders, thus contributing to the success of their global trade endeavors. Remember, being well-prepared is key to navigating the complexities of customs clearance.
?

About Company
Wing Shipping offers various logisticssolutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea, and rail freight. We promote tradebetween China and the world, contributingto the development of your business.