Blog Details

As an experienced freight forwarder in the international logistics field, I am acutely aware of the pivotal role air freight plays in modern trade and logistics. Air freight, as a mode of transportation, is not only fast but also efficient and reliable, making it the preferred logistics solution for many businesses. In this informative blog, I will delve into the key advantages of air freight, helping you understand why it occupies such a critical position in international logistics.
Speed and Timeliness
One of the foremost advantages of air freight is its speed. Compared to sea or land transport, air freight can deliver goods anywhere in the world within a matter of hours to a few days. This is particularly important for time-sensitive goods such as perishable agricultural products, fashion apparel, and urgent medical supplies.
?

?
High Reliability
Airlines typically offer strict flight schedules with accurate arrival times. Compared to other modes of transport, air freight has a higher punctuality rate due to fixed flight timetables and fewer weather-related disruptions.
Safety and Security
Air freight provides better protection for goods. The security checks in air cargo are stringent, reducing the risk of damage and theft. Additionally, packaging requirements for air freight are usually simpler than for sea and land transport, cutting down on additional packaging costs.
Global Network Coverage
Nearly every country and major city has at least one international airport, allowing air freight to cover an extensive network. For situations requiring rapid delivery to remote or hard-to-reach areas, air freight is particularly suitable.
Reduced Inventory and Insurance Costs
Due to the rapid nature of air freight, businesses can manage their inventory more efficiently, minimizing costs associated with long-term storage. Additionally, shorter transportation times reduce insurance premiums.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Air freight can adapt to changing market demands and emergencies. Airlines typically offer a variety of different services and solutions to meet specific transportation needs.
Conclusion
Although the cost of air freight is generally higher compared to other modes of transport, its speed, reliability, safety, and global coverage make it an irreplaceable choice in many scenarios. As freight forwarders, our role is to help clients find the best balance between cost and efficiency, ensuring their goods are delivered safely and swiftly to their destination.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details

In the landscape of a globalized economy, international courier services play an essential role. The Big Four—DHL, FedEx, UPS, and TNT—have become pivotal pillars of global trade and communication with their extensive networks, efficient services, and powerful logistics capabilities. This blog will delve into the service characteristics of these four courier companies and how they shape the world we live in today.
DHL: The Vanguard of Transnational Transportation
DHL is one of the pioneering providers of international courier services, particularly renowned for transnational parcel delivery. With services in over 220 countries and territories, DHL offers flexible transportation solutions for everything from documents to bulk shipments. Its extensive network is particularly influential in Europe and Asia, where DHL has established a dominant presence.
?

?
FedEx: Synonymous with Speed and Reliability
FedEx is globally recognized for its fast and reliable courier services, offering door-to-door delivery solutions. Its "absolutely, positively" philosophy ensures that parcels are delivered on time as promised. A key component of FedEx's competitive edge is its air network, which includes one of the world's largest cargo airline fleets, enabling rapid response to customer needs and ensuring the timeliness of deliveries.
UPS: The Paradigm of Comprehensive Logistics Services
UPS is known for its comprehensive logistics and supply chain management services, providing customers with an array of solutions including transportation, sorting, warehousing, and international trade services. UPS's strength lies in its extensive network in North America and its stable transportation services, along with global parcel and cargo transport offerings.
TNT: A Strong Competitor in the European Market
TNT, now part of FedEx, particularly emphasizes courier services in the European market. Grounded in its land network, it offers speedy next-day services and has a strong reputation for door-to-door express delivery. While TNT's stronghold is in Europe, its services extend globally to various countries and regions.
Conclusion
The Big Four international couriers support the rapid development of global business and personal communication with their vast networks and efficient services. Whether it's documents urgently needed by international business?people, long-distance gifts, or global e-commerce goods, these courier companies provide secure and expedited transportation services. Choosing which courier to use depends on specific needs, including speed of transit, service coverage, cost-effectiveness, and additional services offered. As global economic integration deepens, the role of these four courier giants is set to become even more significant.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details
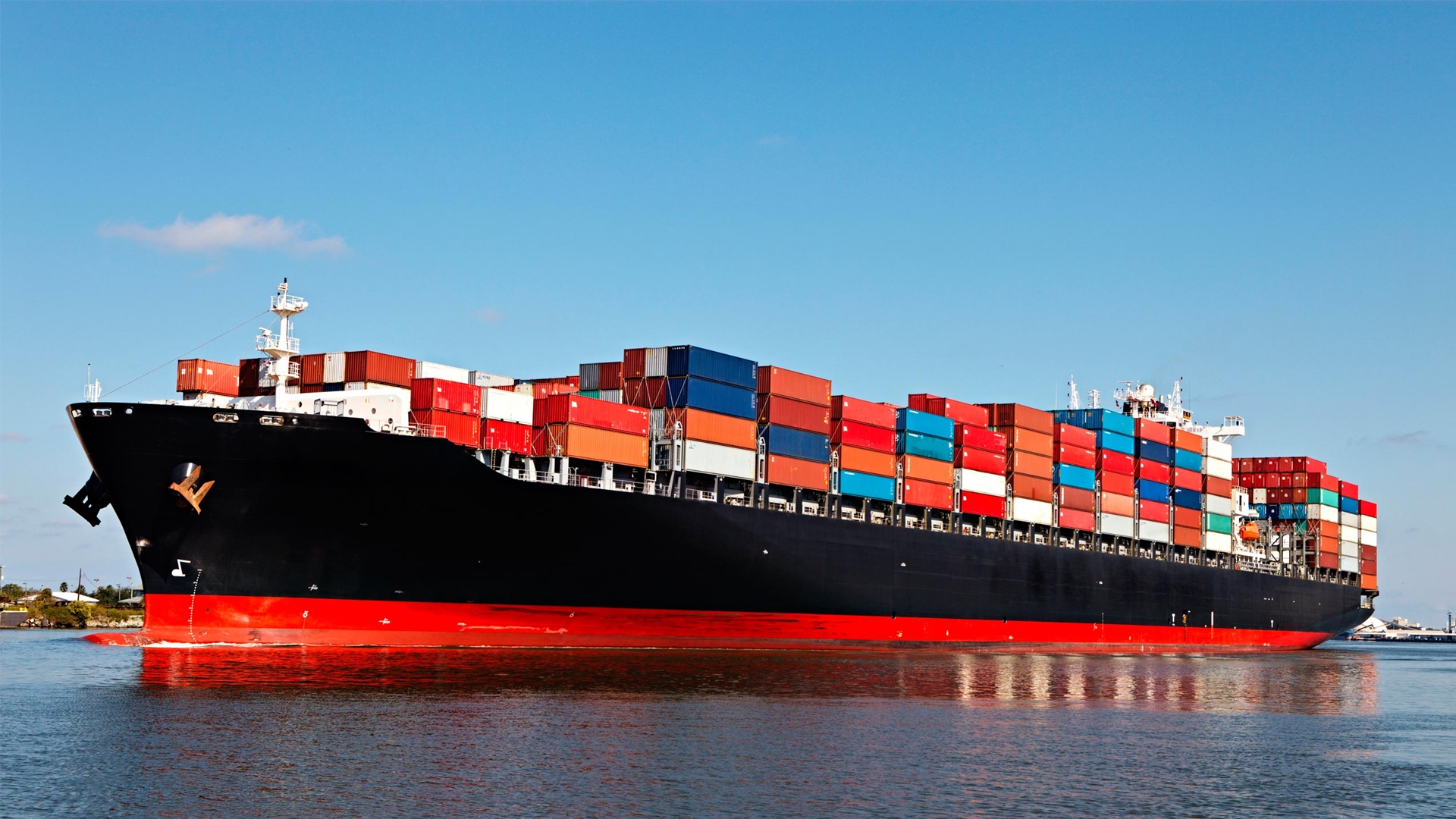

Sea freight?plays an indispensable role in the realm of international logistics, acting as a cornerstone for global trade. From raw materials to finished goods, from foodstuffs to electronics, maritime shipping connects global markets, offering a cost-effective and high-capacity transportation solution. In this blog post, we'll explore the basic process of maritime shipping and its pivotal role in international trade.
The Basic Process of Sea Freight
Cargo Preparation and Pre-Processing
Before being loaded onto a ship, cargo needs appropriate packing and labeling. This includes ensuring that packaging can withstand the rigors of long sea voyages and that all necessary documentation, such as packing lists and commercial invoices, is attached.
Containerization of Goods
Containers are the most commonly used transport unit in maritime shipping. Once the goods are containerized, they are transported to the port and loaded onto a designated vessel.
Vessel Loading and Departure
After the cargo is loaded onto the ship, it embarks on its journey following a predetermined route. During the voyage, the ship may call at multiple ports to load and unload various cargoes.
The Voyage
Throughout the voyage, the ship's speed, route, and safety are managed by experienced crew members and the captain. Modern tracking systems also allow shippers to monitor the real-time location and status of their cargo.
Destination Handling
Upon arrival at the destination, the cargo is offloaded at the port and goes through customs clearance. This process involves paying duties, completing necessary customs declarations, and ensuring all import documentation is in order.
Inland Transportation
Once cleared, the cargo is transported to its final destination, often involving trucks, railways, or other forms of land transportation.

?
Advantages of Sea Freight
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to air and land transportation, maritime shipping is usually a more economical choice, especially for bulk goods.
High Capacity: Sea freight can handle large volumes of cargo, making it ideal for heavy or voluminous goods.
Environmental Friendliness: Relative to other modes of transport, Sea freight has a lower carbon footprint.
Challenges of Sea Freight
Slower Speed: Sea freight has a higher time cost compared to air transport.
Dependence on Port Infrastructure: Sea freight?relies heavily on port facilities for loading, storage, and transportation.
Potential Delays: Due to various factors such as weather and port congestion, Sea freight?can experience delays.
Conclusion
Sea freight?is a vital pillar of international trade and logistics, offering a high-capacity, cost-effective mode of transportation. Although it may not be as fast as air transport, its role in global trade is irreplaceable. Understanding the process of Sea freight?can help businesses and individuals better plan and execute international transport, ensuring that goods reach global destinations safely and efficiently.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details
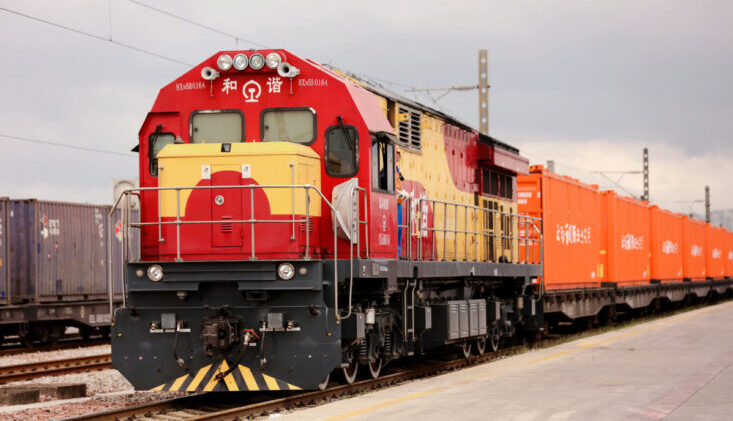

In the global trade landscape, Eurasian rail transport plays an increasingly vital role. Spanning across Asia and Europe, this railway link is not just a physical connector between two continents but also a crucial channel for economic cooperation and cultural exchange. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of Eurasian rail transport, its advantages, and how it impacts international logistics and trade.
The Rise of Eurasian Rail Transport
With the advancement of the Belt and Road Initiative, the Eurasian railway network has seen significant development. This route, connecting China, Central Asian countries, Russia, and Europe, offers a fast and reliable option for cargo transportation to countries along its path.
?

?
Advantages of Eurasian Rail Transport
Time Efficiency
Compared to sea transport, the Eurasian rail route is shorter in time, often completing journeys within two weeks, whereas sea transport usually takes a month or longer.
Cost-Effectiveness
While air transport is faster, it is also more expensive. Rail transport provides a more cost-efficient alternative, especially suitable for goods that are not ideal for sea transport.
Environmental Friendliness
Rail transport emits less carbon compared to air and sea transport, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Reliability and Safety
Due to its fixed routes and timetables, Eurasian rail transport is generally more reliable and safer compared to other modes of transport.
Challenges in Eurasian Rail Transport
Despite its many advantages, Eurasian rail transport also faces challenges, such as differences in railway standards and transport regulations between countries, complexity in cross-border procedures, and geopolitical influences.
Future Outlook
In the future, with further improvements in infrastructure and deeper international cooperation, Eurasian rail transport is expected to become an even more important component of international trade. It not only facilitates the flow of goods but also deepens economic cooperation and cultural exchanges between countries along its route.
Conclusion
Eurasian rail transport is a key component of international logistics and global trade. As the global trade landscape continues to evolve, this transport route is set to expand its influence, providing an efficient and reliable corridor for trade between Asia and Europe. As more businesses and countries recognize its potential value, we can expect this mode of transport to play an even greater role in the future.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details

In the intricate world of international trade, freight forwarders are vital cogs in the wheel of global commerce. These agents play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient movement of goods across international borders. In this blog, we will explore the role and importance of freight forwarders in international trade, shedding light on how they facilitate global business transactions.
Understanding the Role of Freight Forwarders
Freight forwarders are specialized agents who act on behalf of importers and exporters to organize the safe, efficient, and cost-effective transportation of goods. They are not typically responsible for physically moving the goods themselves but instead use their expertise to arrange various transportation services and navigate the complexities of international shipping.
?

?
Key Functions of Freight Forwarders
Logistics Coordination: Freight forwarders handle logistical challenges involved in transporting goods from one point to another. This includes selecting and negotiating with carriers, arranging for transport, and scheduling shipments.
Documentation and Compliance: They manage vital documentation such as bills of lading, export and import documents, and customs clearance paperwork, ensuring compliance with domestic and international regulations.
Insurance and Risk Management: Freight forwarders provide or arrange insurance services to protect the value of the goods against loss or damage during transit. They also advise on risk management strategies.
Supply Chain Consultation: Offering expert advice on optimizing supply chains, freight forwarders help businesses strategize to minimize costs and maximize efficiency.
The Importance of Freight Forwarders
Facilitating Global Trade: Freight forwarders are crucial in bridging gaps between buyers and sellers in different countries, enabling seamless international trade.
Navigating Complex Regulations: With trade laws and regulations constantly evolving, freight forwarders stay abreast of these changes, ensuring shipments comply with all legal requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness: Their expertise and network help in negotiating better rates and finding the most economical routes and modes of transport.
Problem-Solving: Freight forwarders are adept at handling unforeseen issues such as delays, rerouting, or paperwork errors, ensuring minimal disruption to the supply chain.
?
Conclusion
Freight forwarders are indispensable in international trade, offering invaluable expertise and services that facilitate the smooth flow of goods across borders. Their role in navigating the complexities of global logistics, from compliance and documentation to cost management and logistical coordination, cannot be overstated. As global trade continues to grow and evolve, the demand for skilled and efficient freight forwarding services will only increase, further highlighting their critical role in the world economy.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details

In the complex and ever-changing realm of international trade, selecting the right freight forwarder is crucial to ensure that your goods are transported smoothly and efficiently to their destination. Freight forwarders are responsible for coordinating various modes of transportation and dealing with a multitude of complex documents and regulatory requirements. This blog post will provide a comprehensive guide to help you find the freight forwarder that best suits your needs.
Define Your Requirements
Before searching for a freight forwarder, it's essential to clearly understand your specific needs. Consider the following questions:
- Type of Goods: Do you need to transport special items such as refrigerated goods, hazardous materials, or oversized equipment?
- Scope of Service: Are you looking for international transportation, or is it limited to domestic?
- Frequency of Transport: Is your shipment a one-time requirement or do you need regular transportation?
- Budget Constraints: What is your budget?
?
Research the Qualifications and Experience
Choosing a qualified and experienced freight forwarder is crucial. Consider the following factors:??
- Licensing and Certification:?Ensure that the freight forwarder has legal business licenses and relevant certifications.
- Industry Experience:?Agents with specific industry experience might better understand how to handle your particular needs.
- Market Reputation:?Investigate the forwarder’s reputation through online reviews, industry forums, or recommendations from peers.
?
代理.jpg)
?
Services and Support
A good freight forwarder should offer comprehensive services and support:
- Diverse Service Options: Including options like sea freight, air freight, land transportation, and multimodal transport.
Customer Service: Good customer service and effective communication channels are very important.
- Additional Services: Such as packaging, warehousing, and supply chain management.
?
Compare Prices and Contract Terms
Price is an important factor in choosing a freight forwarder, but it’s not the only one:
- Transparent Pricing: Look for forwarders who offer clear, no-hidden-fee quotations.
- Contract Details: Carefully review contract terms to understand the scope of service, boundaries of responsibility, and any potential additional costs.
- Flexibility: Consider the forwarder’s flexibility in handling emergencies and change requests.
?
Conclusion
Choosing the right freight forwarder is crucial for ensuring the smooth conduct of international trade. By taking into account the factors mentioned above, you can find an agent that meets your requirements, ensuring the safe and efficient arrival of your goods at their destination. Remember, a good freight forwarder is not just a service provider, but a reliable partner in the complex web of trade.
?

About Company
Wing Shipping offers various logisticssolutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea, and rail freight. We promote tradebetween China and the world, contributingto the development of your business.
Blog Details

As an experienced international freight forwarder, I frequently encounter customers' confusion when choosing between trade terms, especially between EXW (Ex Works) and FOB (Free On Board). Understanding the differences between these terms is crucial for optimizing logistics costs and managing risks. Here's my comparative analysis of EXW and FOB from the perspective of a freight forwarder.
Definition of Trade Terms
EXW (Ex Works): This is the most basic form of transaction. Under EXW, the seller only needs to make the goods available at their premises (like factory, warehouse, etc.). From that point, all transportation costs and risks are transferred to the buyer.
?
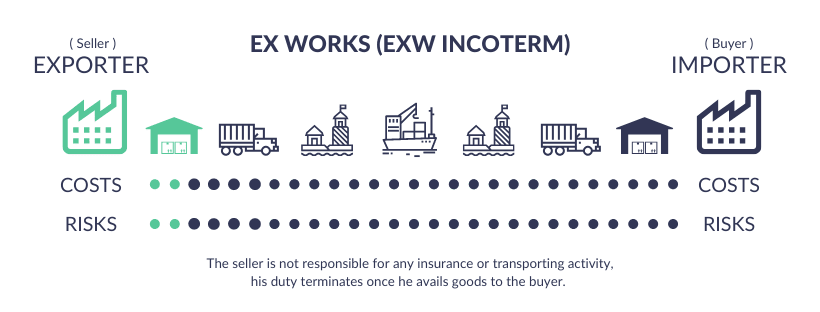
?
FOB (Free On Board): This is a more common international trade term. Under FOB, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a specified loading port and covering all local costs, including export customs clearance. Once the goods are over the ship's rail, the risks and costs are transferred to the buyer.
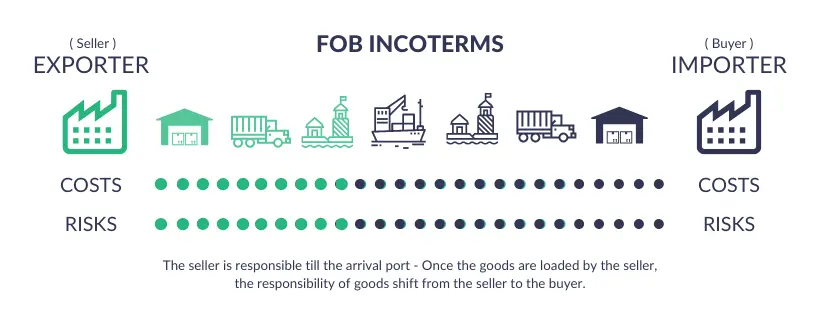
?
Transfer of Costs and Risks
EXW: The buyer assumes all transportation costs and risks right from the seller's factory, including loading, transportation to the port, and export customs clearance.
FOB: The buyer begins to bear all the transportation risks and costs from the moment the goods pass the ship's rail at the loading port.
Role of the Freight Forwarder
Under EXW, as the buyer's freight forwarder, we typically handle the complete logistics chain from the seller's factory to the final destination, including inland transportation, loading/unloading, export customs clearance, etc.
Under FOB, as the buyer's agent, we are mainly responsible for the logistics segment starting from the shipping port, including sea freight, customs clearance at the destination port, and subsequent delivery.
Impact on the Buyer
EXW: The buyer needs stronger logistics control and resources to manage the entire transportation process. Suitable for buyers who want more control over the logistics process.
FOB: More convenient for buyers who do not possess comprehensive logistics management capabilities. The seller takes care of all work up to the shipping port, and the buyer assumes responsibility from sea freight onwards.
Which Is Better?
Choosing between EXW and FOB depends on the needs, resources, and risk-bearing capabilities of both parties. EXW might be more suitable if the buyer wants complete control over the logistics process; FOB might be better if the buyer wants to reduce management burdens and risks.
In conclusion, as a freight forwarder, we advise our clients to consider their logistics capabilities and risk management strategies when choosing trade terms. Understanding the fundamental differences between these terms can help businesses make the best logistics decisions, optimize cost-effectiveness, and reduce potential risks.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details

As a professional freight forwarder, I often encounter clients' confusion when choosing trade terms, especially between DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) and DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid). Understanding the difference between these two terms is vital for ensuring smooth logistics and avoiding unexpected costs. Here's a detailed comparison of DDP and DDU from the perspective of a freight forwarder.
Definition of Trade Terms
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Under DDP, the seller assumes almost all responsibilities and risks for transporting the goods to the buyer's specified location, including transportation costs, insurance, and all import duties and taxes.
DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid): Under DDU, the seller is responsible for transporting the goods to the destination, but not for paying any import duties and other taxes at the destination.
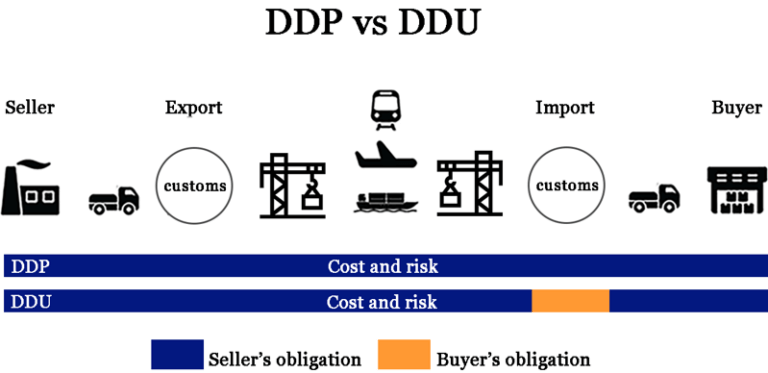
?
Responsibilities and Risks
DDP: The seller bears the highest level of responsibility and risk, including all costs and risks during transportation, as well as the destination country's duties and taxes.
DDU: The seller's responsibility ends with safely transporting the goods to the specified destination, not including payment of import duties and taxes. The buyer needs to take care of this part of the costs and the related customs clearance procedures.
Role of the Freight Forwarder
Under DDP, as the seller's agent, we typically handle the complete logistics chain from start to finish, including customs clearance and paying duties and taxes.
Under DDU, as the seller's agent, our responsibility generally ends once the goods arrive at the destination country's port or airport. The buyer or their agent needs to handle the destination's customs clearance and tax payments.
Impact on Buyers and Sellers
DDP: Suitable for buyers who want to minimize dealing with customs and tax issues in the destination country. Buyers almost don't have to worry about any additional costs when receiving the goods.
DDU: Suitable for buyers willing to handle import processes in their country, especially those who have a clear understanding of local duties and taxes.
How?to Choose?
Choosing between DDP and DDU depends on the parties' desire for control over costs, risks, and customs processes. DDP is more suitable for buyers wanting to simplify operations and avoid the complexity of customs clearance in the destination country. DDU is better for buyers willing to undertake the responsibilities and costs associated with the importing country.
In summary, understanding the differences between DDP and DDU is crucial for international trading parties to formulate suitable logistics and customs strategies. As a freight forwarder, our task is to help clients understand these trade terms and provide corresponding logistics solutions to ensure smooth transactions while minimizing risks and costs.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details

When it comes to international trade, understanding the terms of sale is crucial for the smooth execution of transactions and shipments. Among the myriad of Incoterms, CFR (Cost and Freight) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) are two that often confuse. Both relate to the shipping terms used in the sale of goods when crossing international waters, yet they have distinct differences that can significantly impact the responsibilities and risks of exporters and importers. In this blog, we'll demystify these terms and help you understand which one might be best suited for your trade needs.
What is CFR?
CFR, or Cost and Freight, is an Incoterm where the seller is responsible for the cost of transporting goods to the destination port. Under CFR, the seller must arrange and pay for the transportation of the goods until they reach the port of destination chosen by the buyer. Once the goods have been loaded onto the shipping vessel, the risk of loss or damage to the goods transfers from the seller to the buyer. Therefore, it's the buyer's responsibility to insure the goods from the point of departure.
?
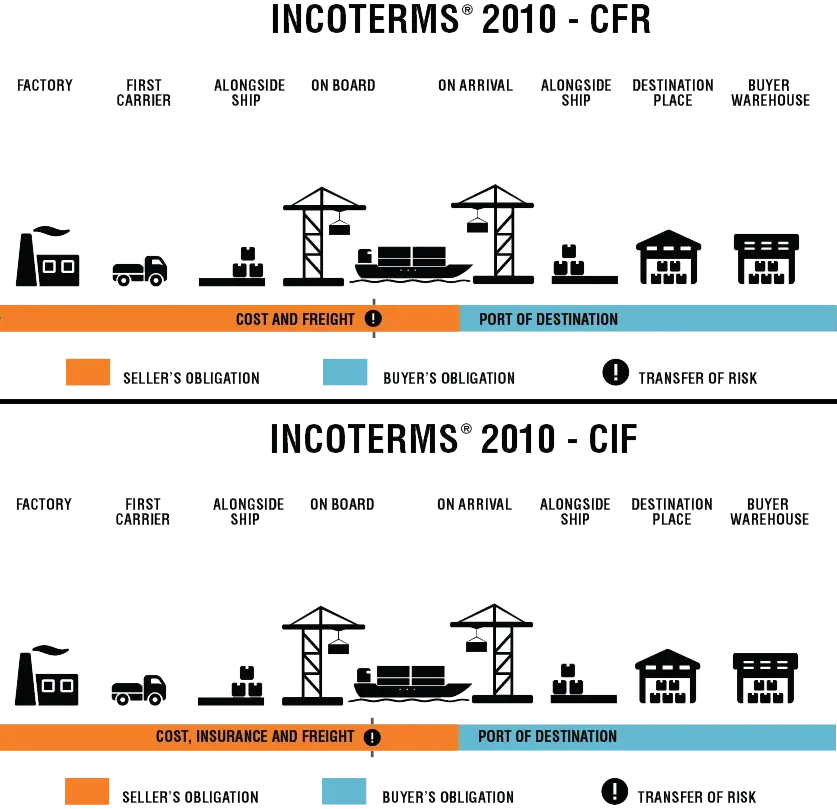
?
Key Points for CFR:
Seller pays for transportation to the destination port.
Risk transfers to the buyer once goods are on board the vessel.
Insurance during transit is the buyer's responsibility.
What is CIF?
CIF, or Cost, Insurance, and Freight, is one step further than CFR. Not only does the seller cover the costs and freight to get the goods to the destination port, but they also pay for the insurance during the sea transit. The transfer of risk is the same as CFR—the seller’s risk ends when the goods are on board the vessel. However, with CIF, the seller has to procure marine insurance against the buyer’s risk of loss or damage to the goods during the carriage.
Key Points for CIF:
The seller pays for transportation and insurance to the destination port.
Risk transfers to the buyer once goods are on board the vessel, but the seller procures insurance.
The seller's responsibility includes insurance coverage for the goods until the destination port.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between CFR and CIF often depends on the agreement between buyer and seller and who wants to take on the insurance responsibility. Here's what to consider:
When to Choose CFR:
If the buyer can obtain insurance at a more competitive rate.
When the buyer has better control over the insurance process.
If the buyer wishes to manage the risk from the port of origin.
When to Choose CIF:
If the seller has better access to insurance options.
When the seller can bundle insurance with freight for better rates.
For buyers who prefer an all-inclusive price and would rather not deal with insurance separately.
Implications of CFR and CIF
Understanding the implications of CFR and CIF is paramount, especially when negotiating contracts. Here are some further considerations:
Insurance Coverage: Under CIF, sellers must obtain insurance only for minimum coverage. Buyers may need additional coverage for their goods.
Cost Control: CFR can potentially offer more cost control to the buyer since they are responsible for the freight and insurance arrangements.
Convenience: CIF is often seen as more convenient for the buyer since the seller arranges most of the shipping logistics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while CFR and CIF may appear similar at first glance, the differences, particularly regarding insurance, are significant. Sellers and buyers must carefully consider these terms and choose the one that aligns with their needs and provides the most strategic advantage. As with all international trade dealings, it's recommended to consult with a legal or trade expert before finalizing any agreements. Whether you opt for CFR or CIF, a clear understanding of the terms will help you navigate the complexities of global trade with confidence.
?

About Company
QIFLY offers various logistics solutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea freight and express. We promote trade between China and the world, contributing to the development of your business.
Blog Details

In today's international trade and logistics realm, multimodal transportation has emerged as a key connector of global markets. This method involves effectively combining different modes of transportation, such as sea, air, rail, and road, to optimize the efficiency and cost of the entire logistics chain. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of multimodal transportation, its advantages, and how it plays a pivotal role in modern logistics.
Understanding Multimodal Transportation
Multimodal transportation refers to a comprehensive transport method that involves at least two different modes of transport, thereby achieving seamless integration within the global transportation network. This approach is typically coordinated by professional logistics companies or freight forwarders under a unified transport contract to ensure the smooth transit of goods from the origin to the destination.

?
Advantages of Multimodal Transportation
Cost-Effectiveness
By leveraging the strengths of different transport modes, multimodal transportation finds an optimal balance between cost and efficiency. For example, sea transport is cost-effective, air transport is fast, and rail and road transport is flexible for short distances.
Time Efficiency
Multimodal transportation significantly increases transport efficiency by optimizing routes and reducing waiting times for goods during transshipment.
Environmental Friendliness
By reducing the proportion of air and road transport, and increasing the use of rail and sea transport, multimodal transportation helps decrease overall carbon emissions, aligning with sustainable development goals.
Reduced Transportation Risks
Multimodal transportation reduces the risk of loss and damage to goods during transshipment through professionalized management.
Applications of Multimodal Transportation
Let's take a practical example: a batch of goods needs to be transported from China to Europe. The goods are first shipped by sea from a port in China to a major port in Europe and then transported by rail or road to their final destination. This method is more economical than sole reliance on sea or air transport and faster than complete dependence on land transport.
Conclusion
Multimodal transportation is an integral part of modern international logistics, offering an efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution by integrating the advantages of different transportation modes. For businesses looking to optimize their supply chain, reduce transportation costs, and increase efficiency, multimodal transportation is a viable option. As global trade continues to evolve and environmental conservation becomes increasingly important, the role of multimodal transportation is set to become even more significant.
?

About Company
Wing Shipping offers various logisticssolutions for Chinese exports, including air,sea, and rail freight. We promote tradebetween China and the world, contributingto the development of your business.